To aid in the complete evaluation of the eye and visual system, we have an array of diagnostic capabilities. Below are examples of such studies performed in an office setting.
These include:
- REFRACTION: To determine the amount of nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism of the eye. Generally a part of a comprehensive exam or when glasses are needed.
- CORNEAL TOPOGRAPHY: To analyze the curvature of the cornea for diseases such as corneal warpage syndrome, keratoconus, for patients undergoing lasik surgery, and for evaluation of high astigmatic disorders.
- GONIOSCOPY: A painless procedure for the evaluation of the “angle” of the eye, generally used when glaucoma is suspected or when there’s elevated fluid pressure in the eye.
-
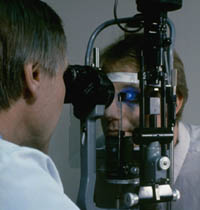
Applanation Tonometry of a patient during a comprehensive exam. The procedure is painless and is highly accurate in measuring intraocular pressure.
APPLANATION TONOMETRY: A painless method of measuring intraocular pressure and is included in a full comprehensive examination. Dye is instilled into the eye, and a cobalt blue filter light used in the measuring of pressures.
- VISUAL FIELDS: A special analysis of the entire visual field space for the evaluation of glaucoma, optic nerve and neurologic disease.
- A-SCAN: Measurement of the length of the eye and distances between intraocular structures. Also used in calculating intraocular powers in preparation for cataract surgery.
- B-SCAN: Evaluation of intraocular structures and orbit for retinal detachment, intraocular hemorrhage, and intraocular tumors.
- FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY: A special dye study of the retinal circulation for diseases such as macular degeneration, diabetic eye disease, and other related problems of the retina.
NORMAL FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAM of corresponding photo below showing the optic nerve and lighting up the blood vessels. The thinner vessels are arteries carrying blood to the retina, and the thicker vessels are veins, carrying blood back to the heart. The dark spot in the center is the macula, which is responsible for “center” vision. (Please see macular degeneration for more information.)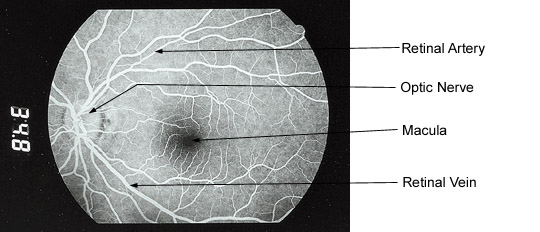
- FUNDUSKERATOMETRY: For “routine” evaluation of the corneal curve in contact lens management
and other minor disorders involving corneal curvature.
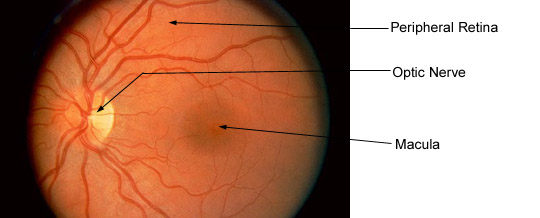
NORMAL PHOTOGRAPH OF THE BACK OF THE EYE. To the left is a yellowish round structure called the optic nerve. It is not a true nerve, but actually an extension of the brain itself. The dark spot in the center is called the macula which is responsible for center vision, and is the part of the retina affected in macular degeneration.
- EXTERNAL OCULAR PHOTOGRAPHY: A necessary part of evaluation and follow up care for a variety of diseases involving the front and back parts of the eye.
